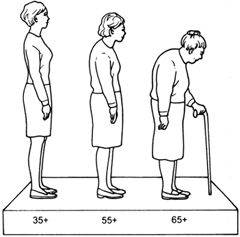
 Osteoporosis is a natural part of aging. The bones becomes thinner as a person ages. They are therefore more brittle and easily fractured. However, this condition may be worsened by a diet deficient in calcium which is essential for bone health. Osteoporosis is more common in females as calcium may be removed from their skeletons in child bearing years.
Osteoporosis is a natural part of aging. The bones becomes thinner as a person ages. They are therefore more brittle and easily fractured. However, this condition may be worsened by a diet deficient in calcium which is essential for bone health. Osteoporosis is more common in females as calcium may be removed from their skeletons in child bearing years.
Rickets is a disease which occurs in children. It results in the bones becoming deformed. The most common cause of rickets is insufficient vitamin D or calcium in the diet. The symptoms include bow legs, deformed spine and bones that fracture easily.. Rickets rarely occur nowadays because of improved diets
Source: Dairy produce, green veg. nuts, tofu, fortified bread & white flour, canned fish
Function: – Formation of healthy bones and teeth, blood clotting and nerve function
Deficiency: – Rickets-deficiency disease affecting children
– Osteomalcia-affects adults
– Osteoporosis-brittle bones in later life
Absorption
|
★★★ osteoporosis in ireland★★★
Healthy bones are like banks, the more deposits you make, and the more withdrawals you can count on. Diet plays a major role in ensuring healthy bones. In particular, Calcium and Vitamin D need to be taken in the right amounts through life to build bone and slow down bone loss. Eating a healthy balanced diet, containing adequate calories, can help to improve your overall bone health not to mention your overall health.
Bone development
It is important to look after your bones no matter what your age. While 90% of adult bone is laid down by the age of 17, bone continues to grow in strength up until the mid-thirties. After this, it is natural to lose a small amount of bone each year. This is accelerated in women after the menopause when the protective effect of oestrogen is lost. However, calcium, Vitamin D and regular exercise help maintain bone strength and minimise bone loss.
★The Department of Health and Children recommend that children,★ adults and older people include three servings of calcium rich foods per day
The easiest way to obtain this is through the regular consumption of milk, cheese and yogurt i.e. 3 servings each day from the milk group of foods. Teenagers and pregnant women need five servings each day.A serving is equal to:
A glass of milk an ounce {matchbox size} of cheese
Teenagers in particular need 5 servings of calcium each day to meet the requirement for growth and development. Unfortunately, 75% of teenage girls do not meet their calcium needs. Other factors that may have a negative effect on bone health at this time include: lack of exercise, smoking, alcohol and lack of exercise, smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet or some weight loss diets, and eating disorders such as anorexia and/or bulimia. Excessive consumption of fizzy drinks in teenagers means that healthier more nutritious drinks like milk and juices are often displaced in the diet leading to poor calcium intakes.
Tips to boost calcium intake
Dairy products are extremely versatile and can be included in the diet in many ways. Cooking does not destroy calcium, so it could not be easier to get your recommended number of servings each day. Serving suggestions include
A bowl of breakfast cereal with milk cheese on crackers or toasted cheese sandwich fruit salad with yogurt
★★★Definition of osteomalacia ★★★
Osteomalacia refers to a softening of your bones, often caused by a vitamin D deficiency. Soft bones are more likely to bow and fracture than are harder, healthy bones.
Osteomalacia is not the same as osteoporosis, another bone disorder that also can lead to bone fractures. Osteomalacia results from a defect in the bone-building process, while osteoporosis develops due to a weakening of previously constructed bone.
Muscle weakness and achy bone pain are the major symptoms of osteomalacia. Treatment for osteomalacia involves replenishing low levels of vitamin D and calcium and treating any underlying disorders that may be causing the deficiencies.
Hypervitaminosis A refers to any number of a large amount of toxic effects from ingesting too much preformed vitamin A. Symptoms may result from effects, including altered bone metabolism and altered metabolism of other fat-soluble vitamins. Hypervitaminosis A is believed to have occurred in early humans and the problem still persists.
Toxicity may result from ingesting too much preformed vitamin A from the diet, supplement intake, or prescription medication, and can be prevented by not ingesting more than guideline amounts.
Diagnosis is difficult, as serum retinol is not sensitive to toxic levels of vitamin A, although some tests are available. Hypervitaminosis A is usually treated by stopping high vitamin A intake. Most people fully recover.
High intake of provitamin carotenoids, such as beta carotene, does not cause hypervitaminosis A, as conversion to the active form of vitamin A is highly regulated.
It is important not to forget to link your source of information. Is this in your own words, can you simplify it down? Maith thú an obair déanta agat.
****Hypovitaminosis****
**Hypovitaminosis A**
Hypovitaminosis A (also known as Follicular Hyperkeratosis and “Phrynoderma” which means Toad Skin) is common in children in the developing world, most often associated with diseases of fat malabsorption.
It is seen as rough, hyperkeratotic, follicular papules on the skin of elbows and knees.
**Hypovitaminosis D**
Hypovitaminosis D is a deficiency of vitamin D. It can result from inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D and/or inadequate sunlight exposure (in particular sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays), disorders limiting vitamin D absorption, and conditions impairing vitamin D conversion into active metabolites—including certain liver, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone softening diseases as rickets in children and osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults. Emerging evidence suggests vitamin D plays a role in NAFLD pathogenesis.
★Osteoporosis in ireland★
Osteoporosis can affect the whole skeleton, but the most common areas to break are the wrist, spine and hip. The disease affects all age groups and both sexes – it is not just a female or old person’s disease.
At present it is estimated that 300,000 people in Ireland have Osteoporosis. One in 5 men and 1 in 2 women over 50 will develop a fracture due to Osteoporosis in their lifetime. The disease can affect even children.If you have one fragility (low trauma) fracture, this doubles your risk of another fracture due to Osteoporosis.However, it can be prevented in most cases, and is a treatable disease in the majority of people. Early diagnosis is essential for the best results. A DXA scan of your spine and hip area is the gold standard for diagnosing Osteoporosis and is highly recommended if you are at risk.
Signs of Osteoporosis
Usually the first sign of Osteoporosis is a fragility (low trauma) fracture e.g. a broken bone due to a trip and fall from a standing position or less.
Sudden, severe episodes of upper, middle or low back painDevelopment of a hump on the back and / or a change in body shape, for example, the rib cage may rest on pelvic rim or a pot belly develops .Most people have no pain till a fracture occurs but a small percentage of people can have back or hip pain, prior to a fracture.
Very good work, clear and to the point. It is important not to forget to link your source of information. Is this in your own words? Maith thú. What is the RDA of Calcium and Vit D?
What does hypovitaminosis mean? Hypovitaminosis means Any of several diseases caused by deficiency of one or more vitamins. malnutrition (a state of poor nutrition which can result from insufficient or excessive or unbalanced diet or from inability to absorb)
What does Hypervitaminosis mean?The term ‘hypervitaminosis’ means an abnormal condition resulting from taking vitamins excessively; can be serious for vitamins A or D or K.
Down below are some websites of pictures got to do with Hypervitaminosis and Hypovitaminosis.
*http://www.ovguide.com/hypervitaminosis-9202a8c04000641f80000000003bef96
*http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypovitaminosis_D